ESM Server Installation Guide - Windows¶
Important note
It is recommended that you review the document titled Functional Overview of ESM before continuing with the tasks outlined here.
System Requirements¶
Hardware Requirements¶
Provisioning a standalone host to run the ESM Server component is advisable. The following host specifications are recommended:
- Minimum 4 CPUs or vCPUs
- 10GB RAM
- 2GB System Storage for the ESM Server binaries and logs
- 50 – 100GB Storage for the underlying ESM Database tablespace
Larger deployments with an increased number of end users, jobs or nodes may require more resource. If in doubt, contact Boemska Support for assistance when sizing the ESM Server host.
Supported Versions of Windows¶
- Windows Server 2008 32bit (Service Pack 1 minimum)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 64bit (Any Service Pack)
- Windows Server 2012 64bit (Any Service Pack)
The following platforms are also known to work with ESM Server (for testing purposes):
- Windows XP Professional SP3 32bit
- Windows 7 64bit
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
Supported Databases¶
- A standalone database installation is no longer required.
Note on supported databases
As of March 2018, support for third party databases is being phased out in favour of the embedded ESM Database (currently based on PostgreSQL 9.5). The embedded ESM database ships with the ESM Server binaries, and provisioning of a standalone database component is no longer required. For legacy documentation on MySQL or Oracle based deployment methods please contact Boemska Support.
Installation Requirements¶
-
Approximately 1.5GB disk space for the ESM Server installation files
- ESM Server Installer compressed (318MB)
- ESM Server Installer unpacked (390MB)
- ESM Server Installed (775MB)
-
50GB – 100GB disk space/tablespace for selected database storage
- Storage requirements vary depending on the number of nodes and sessions/jobs monitored
- ESM data collection intervals and metric resolutions are configurable, both of which affect the storage required
- ESM has a configurable automated maintenance schedule to manage and maintain storage
- Where possible, Boemska recommends dynamically sized disk space/tablespace which can be adjusted according to demand.
- For a more detailed break down of storage requirements, or if you have a complex/large environment please contact Boemska for further information
-
Ports – If a firewall is configured, the following ports will need to be opened for communication between the ESM Agent(s) and the ESM Server. The default ports are listed below, custom ports can be specified during installation if required
- 18080 – default HTTP port for ESM communication
- 18181 – default HTTPS port for ESM communication
- 14848 – default ESM administration port
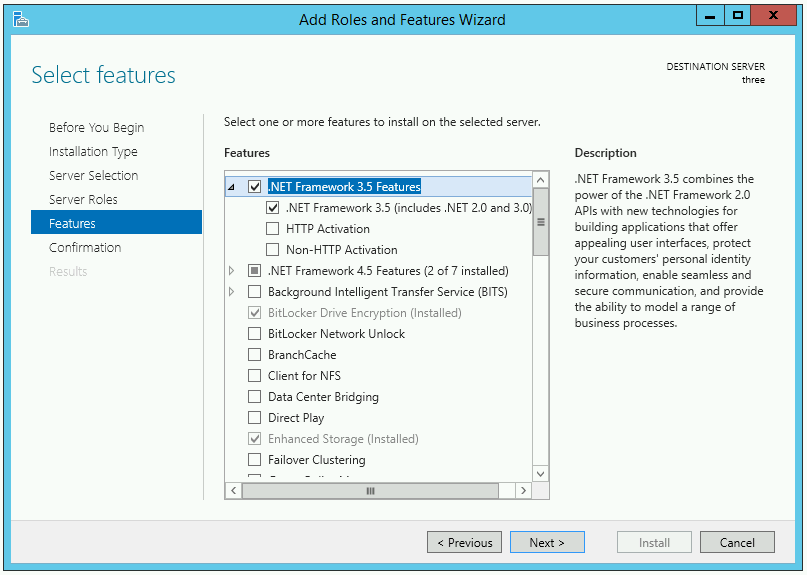
.NET Framework 3.5 (Including .NET 2.0 and 3.0)¶
The .NET Framework packages are required by the ESM Server Installation Wizard. On later versions of Windows Server (2012 onwards), they can be enabled using the Add Roles and Features Wizard.
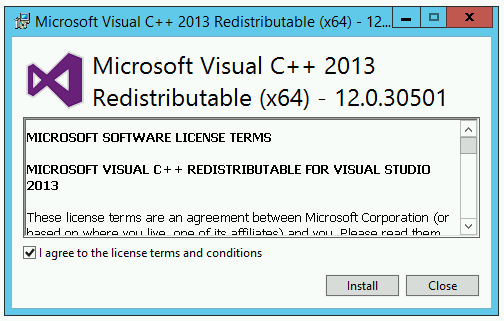
Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Packages¶
The Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Packages are required by the ESM Embedded Database (PostgreSQL 9.5). A version is included with the ESM Server packages, under third_party/vcredist_x64.exe. Alternatively, it can be downloaded directly from the Microsoft website.
Ports¶
If a firewall is configured, the mandatory ports in the following table will need to be opened for communication between the ESM Agent(s) and the Server. The default ports are listed below. Custom ports can be specified during installation if required:
| Port | Description | Mandatory | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18080 | Default HTTP port for ESM communication | Primary inbound and outbound port | |
| 18181 | Default HTTPS port for ESM communication | For embedded HTTPS, not required | |
| 14848 | Default Glassfish administration port | For debug purposes, not required | |
| 15432 | Default Database JDBC connection port | When configuring DB replication |
Note that correct functioning of embedded HTTPS requires manual post-installation configuration of certificates. Configuration with a standalone reverse proxy is also supported. For details contact Boemska Support.
For larger deployments where the ESM Embedded Database is clustered across multiple hosts, more detailed firewall configuration may be required.
User Accounts¶
An Operating System account is required to run ESM Server. ESM requires an account with the following properties:
-
Administrator rights
-
A centrally managed or non-expiring password (recommended)
-
Run as service capability
-
Read and Write access to the target installation directory and sub directories
ESM Server Installation¶
Unpacking the ESM Server Installation package¶
-
Log on to the server using the nominated account with the required installation privileges (see installation requirements for more details)
-
Download the appropriate ESM Server installation package for your Windows operating system. Installation packages can be obtained by signing in to the Boemska Downloads site at https://boemskats.com or by contacting your Boemska representative.
-
Unpack the archive to a suitable temporary location. This guide assumes a target location of
C:\esm-server-installer
Running the Installation Wizard¶
Double-clicking on the esm-server-setup.exe executable will start the ESM Server Installation Wizard.
Note
You may be prompted to grant the ESM Installation Wizard elevated privileges. This is required in order to deploy the ESM Server application as a Windows Service.
-
You will be presented with a Welcome Screen.
 Click Next.
Click Next. -
You will now be presented with a License Agreement. You must agree to the terms set out in the license agreement in order to continue with the installation, by clicking the I Agree button.
-
Next, you will be presented with a choice of database. Unless othewise instructed by your Boemska representative, select the
Embeddedoption.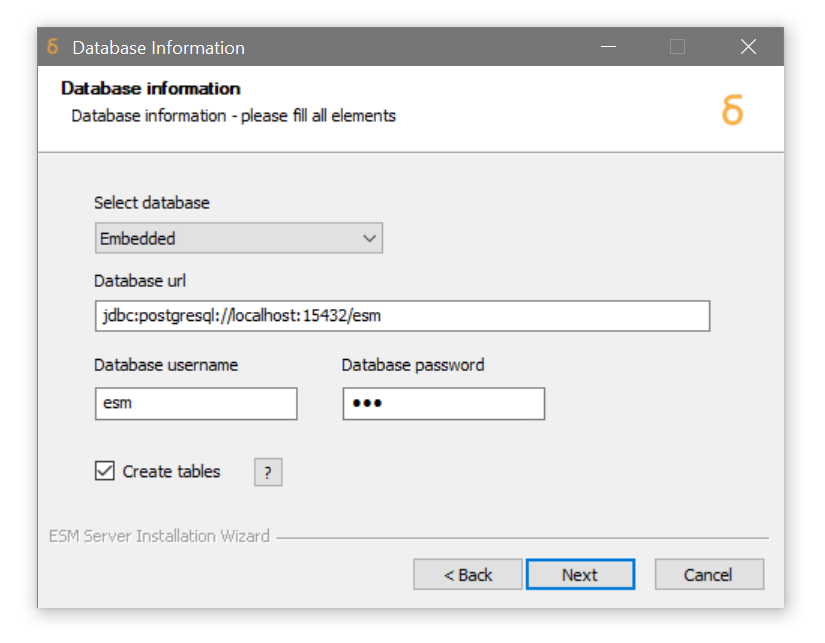
Enter theusernameandpasswordto set the credentials for the embedded database. In most cases, it is sufficient to change the password if required and otherwise using the default values provided. -
The default Embedded database port is 15432. Unless this port is taken by another application running on the local machine, click Next.
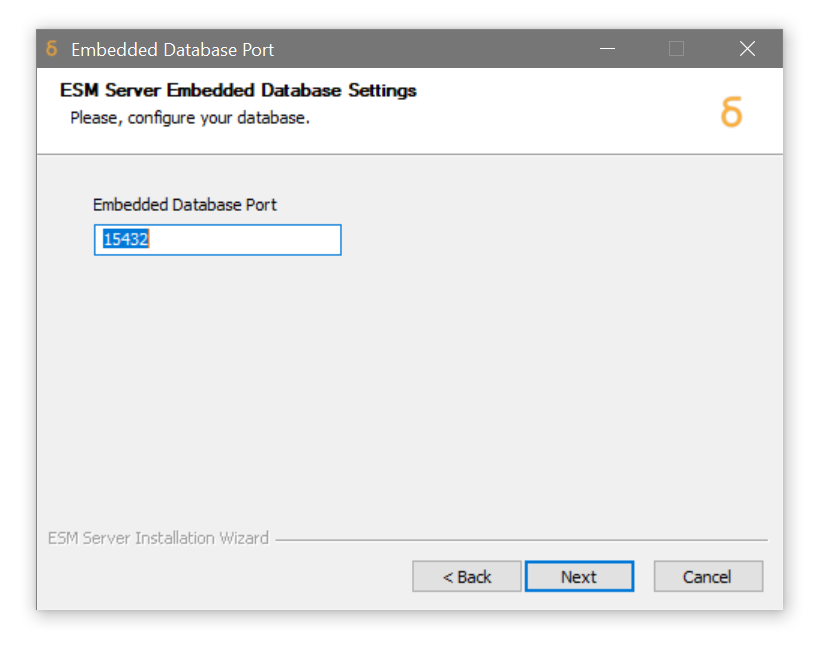
-
Configure the ports you would like the ESM Server Web Application to use when accepting incoming connections. The default ports are recommended, but may be changed if there is a conflict with another application running on the local machine. As per the note above, only the HTTP and optionally the HTTPS port (shown as the default 18080 and 18181 here) need to be externally accessible.
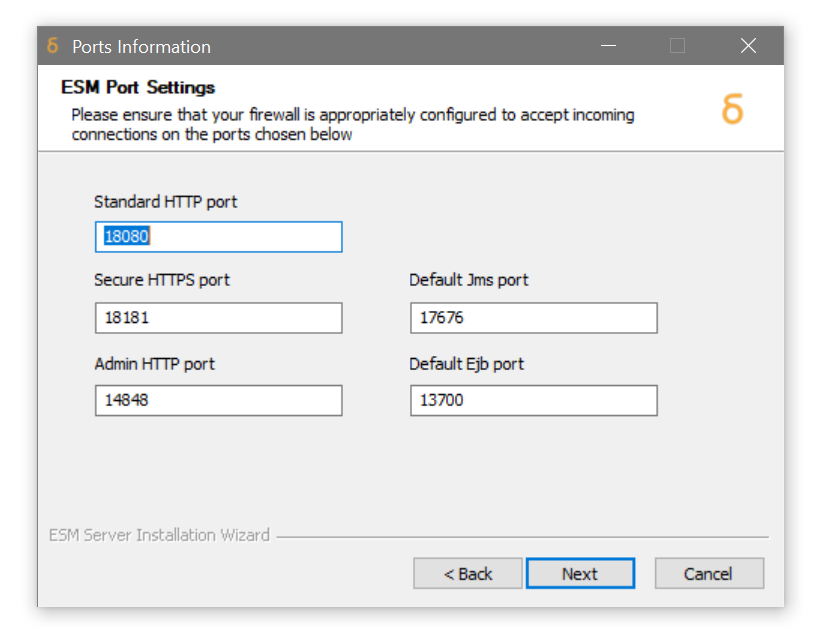
Click Next. -
Choose a Username and Password for the ESM Web Application Administrative User. This is used to access the administrative functionality of ESM via the web browser. Keep these details safe.
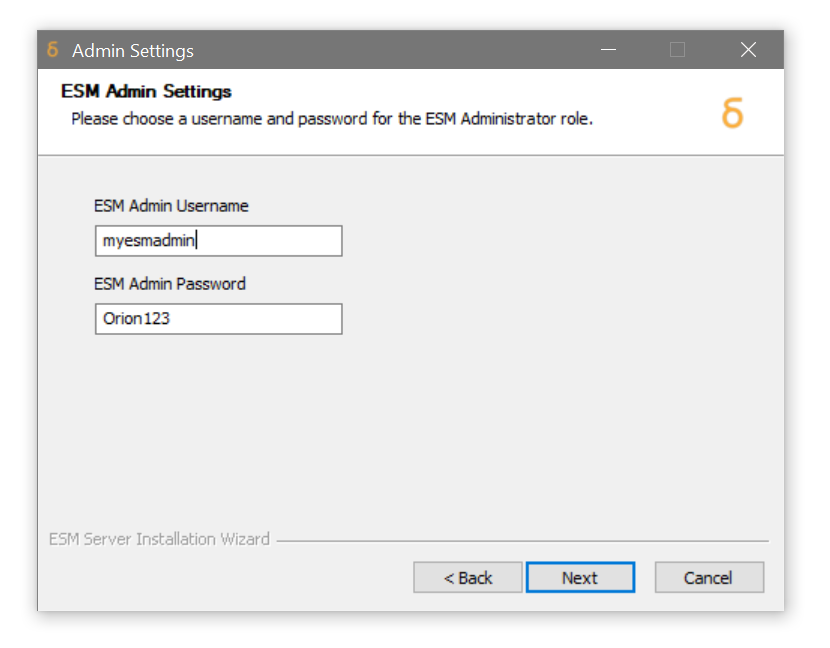
Click Next. -
You are now prompted to create a Windows service for the ESM Server and start it after installation. Service creation is recommended, however this option can be unchecked if you wish to start the ESM Server manually or via another scripted method.
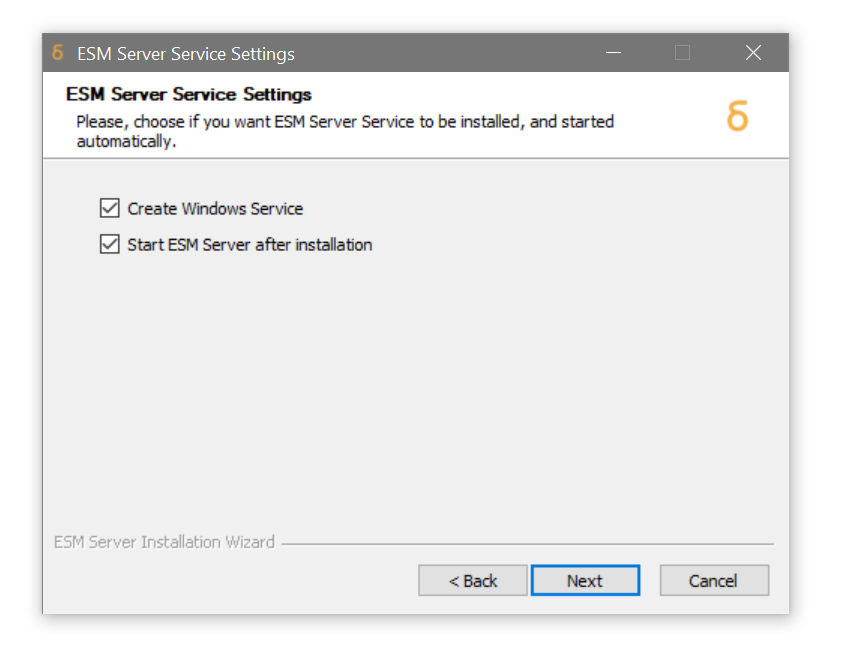
Click Next -
Specify the target install location for the ESM Server using the file browser, ensuring that sufficient disk space is available. A new folder can be created from the browse window if necessary, for example
c:\esm. The installer will automatically create anesm-serversubfolder within the selected destination folder (e.g.c:\esm\esm-server)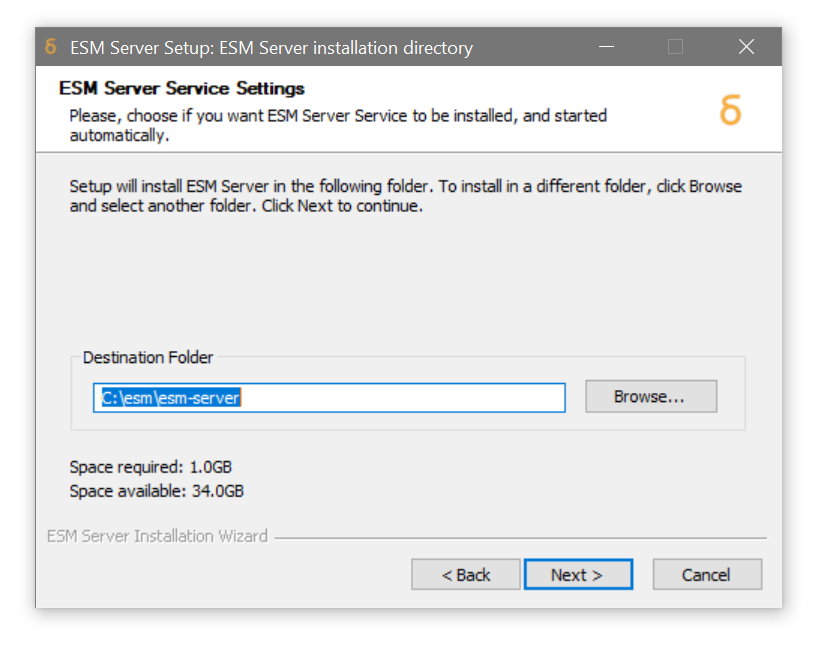
Click Next -
Specify the target install location for the embedded database binaries, if it differs from the ESM server.
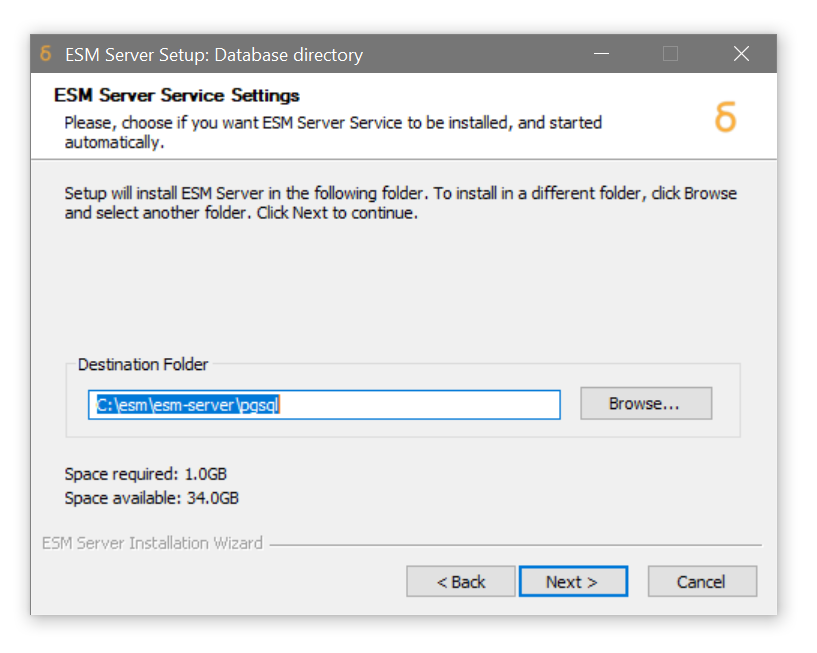
Click Next -
Specify the target location for the embedded database tablespace, if it differs from the ESM server. If you have provisioned a separate location for storage of ESM data, enter it here.
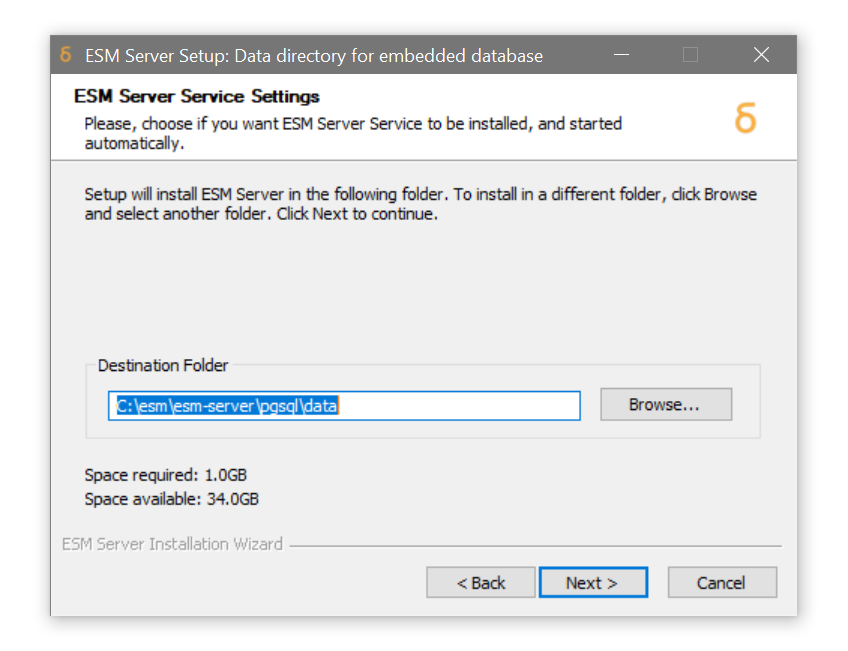
Click Next -
Specify the target location for the embedded database logs. In most cases the default value will suffice here.
Click Install -
The ESM Server installation will now take place. This may take a few minutes. As the services are added they should return a return code of
0, as per the following screenshot. This is the desired result.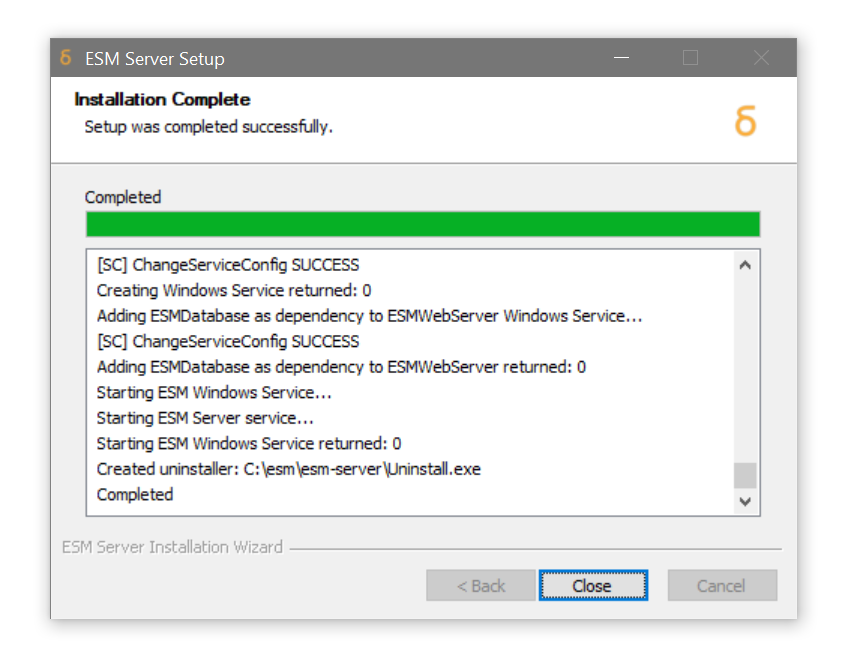
Click Close
Note
It will take up to two minutes for the web interface to become accessible, as the ESM Web Application is deployed into its Application Server for the first time. During this deployment, a java process owned by the ESM installation user will consume a lot of CPU. Once this process has subsided, the application will be ready and accessible via the URL provided.
Updating the ESM License¶
-
Using a web browser, navigate to http://localhost:18080/esm-1.0/ where 18080 is the port you configured ESM Server on. If accessing from a machine other than the server, you must specify the hostname or IP address of the ESM Server in place of
localhost. You should be presented with a screen requesting a license file
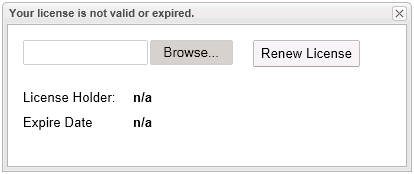
-
Click Browse to navigate and select your ESM license file.
-
Click Upload, then click Renew License.
-
The License Holder and Expiry Date should be updated with the new license details.
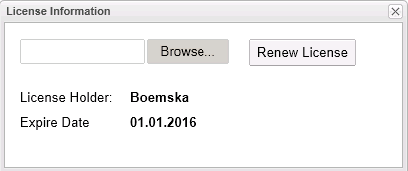
-
Click Refresh. You should see the main ESM Web Application screen.
Validating the Database Connection¶
-
Click on Admin Settings button from the main ribbon (top right)
-
Enter the ESM Administrator username and password you configured during installation
-
Verify that the application is connecting to the database correctly, by checking the reported Database Size:
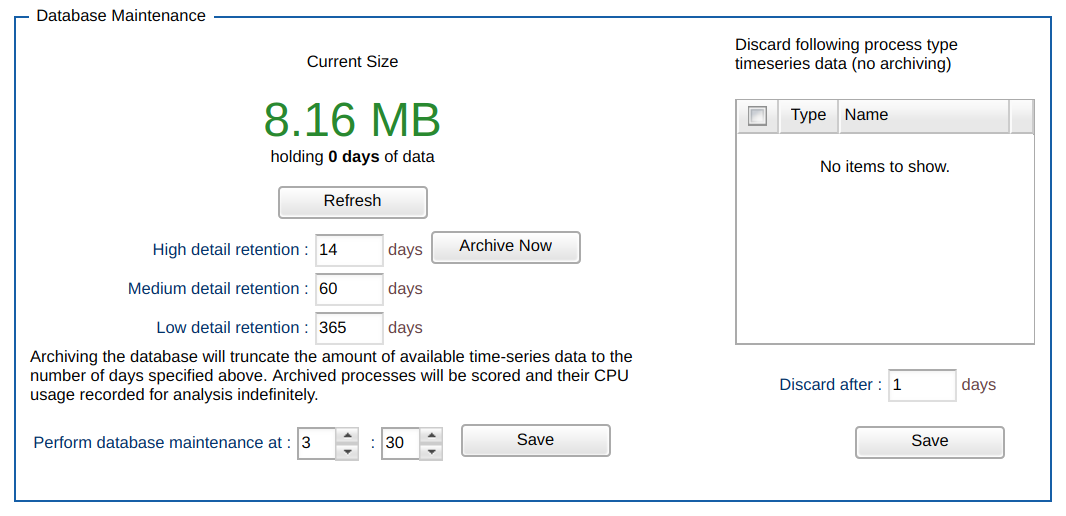 The size of the database should be reported, showing a good connection between the ESM Server and the ESM Database and normal operation of the ESM Server application.
The size of the database should be reported, showing a good connection between the ESM Server and the ESM Database and normal operation of the ESM Server application.
Note
This concludes the ESM Server Installation and Configuration steps. Now proceed with the ESM Agent installation and configuration steps for each node to be monitored, as outlined in the ESM Agent Installation Guide for Unix.
Server Administration¶
Starting and Stopping the ESM Server Service¶
Using Windows Service status¶
If the ESM Server is installed as a service, the service status can be verified using the Windows Services manager. To check the service status, do the following:
-
Click Start
-
In the search box type
servicesto locate the Windows Services manager application -
Right click Services and click Run as Administrator
-
In the services window which appears, scroll down the list to the “ESM Web Server" entry. This should have a status of Started
-
The service can be started and stopped from the Windows Services manager similarly to other services.
Using the Command Line¶
Note
cmd.exe does not support UNC paths. Use Windows Powershell to issue the following commands when the ESM Server installation path is not mapped to a Windows drive letter.
-
Click Start
-
In the search box type
powershellto locate the Powershell program -
Right click the Windows Powershell program and click Run as Administrator
-
At the command prompt, navigate to the location of the installed esm agent binaries. e.g.
cd c:\esm\esm-server\bin -
If ESM Server is installed and running as a Windows Service, the service can be stopped by issuing the "stop-service" command:
If ESM is not installed or running as a Windows Service, it can be stopped by issuing the "stop" command:C:\esm\esm-server\bin> .\esm-server.bat stop-service Stopping ESM Server service...C:\esm\esm-server\bin> .\esm-server.bat stop Stopping ESM Server ... Waiting for the domain to stop .. Command stop-domain executed successfully. -
To start the ESM Server Windows Service from the command line:
Similarly to the stop command above, ESM Server can be started independently of the Windows Service manager by issuing the "start" command:C:\esm\esm-server\bin> .\esm-server.bat start-service Starting ESM Server service...C:\esm\esm-server\bin> .\esm-server.bat start Starting ESM Server ... Waiting for domain1 to start ......................................... Successfully started the domain : domain1 domain Location: C:\esm\esm-server\esm-core\glassfish\domains\domain1 Log File: C:\esm\esm-server\esm-core\glassfish\domains\domain1\logs\server.log Admin Port: 14848 Command start-domain executed successfully.
Inspecting the ESM Server Log Files¶
ESM Server log file is located under the logs path of the installation directory. e.g. C:\esm\esm-server\logs.
By default, minimal logging is enabled for ESM Server to ensure optimum performance running of production environments. More detailed logging can be enabled with the assistance of Boemska Support. For further details please email support@boemskats.com
Uninstalling ESM Server¶
-
First ensure ESM Server by issuing the stop server command. See Starting and Stopping the ESM Server Service for further details
-
Navigate to the installation location ESM Server E.g.
C:\esm\esm-server -
Run the
Uninstall.exeexecutable to uninstall the application.
-
Click Close.